Establish a medical program
Implement a lead-specific medical program supervised by a physician or licensed health care provider (PLHCP) who is knowledgeable about the Cal/OSHA occupational lead standard requirements.
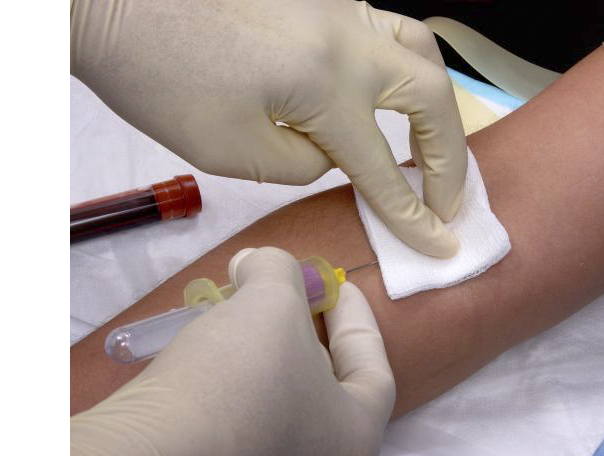
Conduct an initial blood lead level (BLL) test prior to assignment to lead work when worker exposure will be at or above the action level of 2 micrograms per cubic meter (μg/m3), or the worker will perform trigger tasks and an exposure assessment has not been completed.
Perform BLL testing at least every 2 months for the first 6 months of lead work and after any change in task resulting in higher exposure, and every 6 months thereafter. If a worker’s last BLL is at or above 10 micrograms per deciliter (μg/dl), the testing frequency must be increased to at least every two months. Maintain this frequency until two consecutive BLLs taken at least 30 days apart are less than 10 μg/dl.
Notify workers in writing of their BLL test results within 5 working days of receipt. The PLHCP who orders the BLL test also must notify the worker of the test results and recommend follow-up testing and medical examinations.
Temporarily remove workers from exposure to lead who have a BLL at or above 30 μg/dL or 2 BLLs at or above 20 μg/dl. Provide them with alternate work. Before returning to lead work, the worker must have at least 2 consecutive monthly BLL tests taken at least 30 days apart that are below 10 μg/dL.
Implement a written BLL response plan for workers with BLLs at or above 10 μg/dl.
Review the Cal/OSHA Occupational Lead Standards for more information about worker medical surveillance and removal protection requirements, sections (j) and (k).
Learn more:
Lead-safe wash-up facilities and break areas